Generate Target Files
Audio Weaver can generate “Target Files” that can be used with your AWE Core integration. For example, you can compile your Audio Weaver layout to “.aws” which will be a list of all the Server commands that make up your design. You can also generate an “.awb” which is a compiled, binary version of your design that can be stored and executed on your target system.
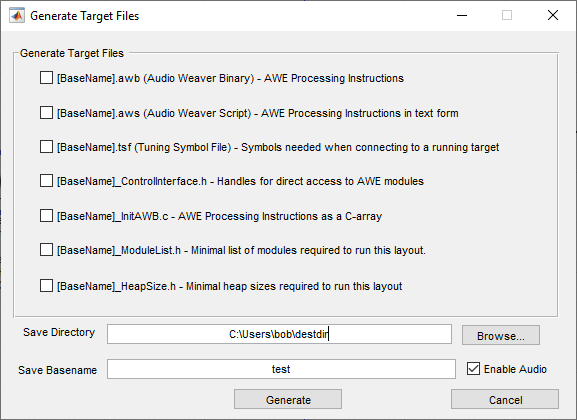
To generate target files, first create a valid design and then select the ‘Tools → Generate Target Files’ menu item. A dialog box will appear and prompt you to choose which files you would like to generate, and where you would like to put them. The “Enable Audio” checkbox will append an audio_pump command to your .AWB and .AWS in case you want to load the design but start the audio processing with a separate server command (for example, start the audio when a button is pressed).
The .h and .c files are used by the target application to load and control the signal processing layout when operating in standalone mode. The .tsf file is used to connect AWE Designer to a target that is running in standalone mode. For more information about how to use these target files, please see the AWE Core 8 Integration Guide.
Attach to Running Target
In some cases, a target may be running a layout that was not loaded via Designer. This may occur, for example, in production hardware where the layout is loaded locally on the target hardware. Designer can still connect and manipulate the layout without interrupting the ongoing processing if a tuning interface is available, and if the .awd and .tsf file (generated via the Generate Target Files dialog described above) for the system are known. This can be extremely useful for troubleshooting.
To Attach to Running Target, load the .awd and generate the tuning symbol (.tsf) file using Designer’s “Tools/Generate Target File” menu item. Connect to the target using the Server’s “Target” menu. Then use Designer’s “Tools/Attach to Running Target” menu item to complete the process.
The layout on the target can now be tuned as if you had loaded it via Designer.
When you are done tuning, the target can be detached by selecting Designer’s “Tools/Detach from Target” menu item.
Module Testing
Module regression tests can be run by selecting the “Tools/Module Tests” menu item. If the ‘Test Modules Used in Layout’ option is selected, the module tests will be run with the exact module configurations used in the layout. This type of testing, called System Test, can be useful to validate that the layout will behave as expected on the attached target.
To run the standard module regression tests on the attached target, the ‘Select Module Group’ dropdown can be used to select which module pack or packs to test. Subsets of the module packs can be run by selecting and de-selecting specific modules in the generated list.
After selecting the “Start Test” button, the tests will execute and results will appear in the “Results” pane. Results can be saved to a .csv file using the ‘Save Results’ button.
Real-Time Profiling
When a layout is running, its computation and memory usage can be measured by selecting the ‘Tools 🡪 Profile Running Layout’ menu item. This will pop up a dialog displaying fine grained profiling information for the entire layout and for each module.
Manual Profiling
In addition to the real-time profiling offered by Profile Running Layout menu, Designer also provides the ‘Tools 🡪 Manual Profile Layout’ tool. The Manual Profiling tool manually pumps each sublayout in a design with tuning commands, which does not rely on any real-time audio interrupts. Collecting data in this way allows for more accurate profiling in certain situations:
Multi-rate Layouts (multiple clockdividers). Because each clockdivided sublayout is typically called in its own thread, the pre-emption of lower priority threads can introduce double-counting while profiling a multi-rate layouts in real time. This can lead to over-estimates of CPU load for sublayouts. Manual profiling pumps each sublayout independently so no pre-emption can occur.
If a layout is exceeding 100% CPU load. Traditional profiling can be inaccurate in this case since audio frames are being missed and not counted towards overall cycles. Since there is no timing requirement when manually pumping layouts, manual profiling can provide accurate CPU loads greater than 100%.
If real-time audio is not available on the connected target. This happens most often when the firmware for the target is still under development, but the CPU load required by a layout needs to be known. Only a tuning interface is required on the target for the Manual Profiling tool to measure CPU load.
Additionally, the Manual Profiling tool allows the user to input an audio file in order to profile the layout under specific scenarios. Both real-time and manual profiling results can be saved to file for later use using the ‘Export to File’ button. Results will be refreshed using the ‘Refresh’ button.
Show Unsaved Changes
To see all the changes since the last save, select ‘Tools Show Unsaved Changes’ for a display using the diff tool the you set in the ‘Global Preferences’ Dialog.
Compare Layouts
Two layouts can be compared by selecting the ‘Tools Compare Layouts’ menu item and selecting the awd files associated with the layouts.
Measurements
Many modules have associated frequency responses. The measurement dialog measures the composite frequency response between two points in your signal processing layout. To set up a measurement, first place marker modules at the beginning and end points of the desired measurement path in the layout.
Then select the ‘Tools Measurement New Measurement’ menu item to get to the measurement dialog.
Here you can select all the properties of the measurement display. When you push the OK button, an editable measurement graph will be displayed.
Tuning Interface Test
This function performs diagnostic measurements on the tuning interface that carries commands from the AWE Server to the target. This is handy to have when porting AWE Core to a new target. The functionality can be accessed via the ‘Tools Tuning Interface Test’ menu item. Test results indicate the interface speed under various conditions. For more information, see the user forum at www.dspconcepts.com.